Myopia
Featured Expert
What is myopia?
Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is a common refractive error where distant objects appear out of focus. Nearsightedness occurs either because the eyeball is too long, or because the eye’s refractive power is too strong due to the shape of the cornea (lens) inside the eye.
Symptoms of Myopia
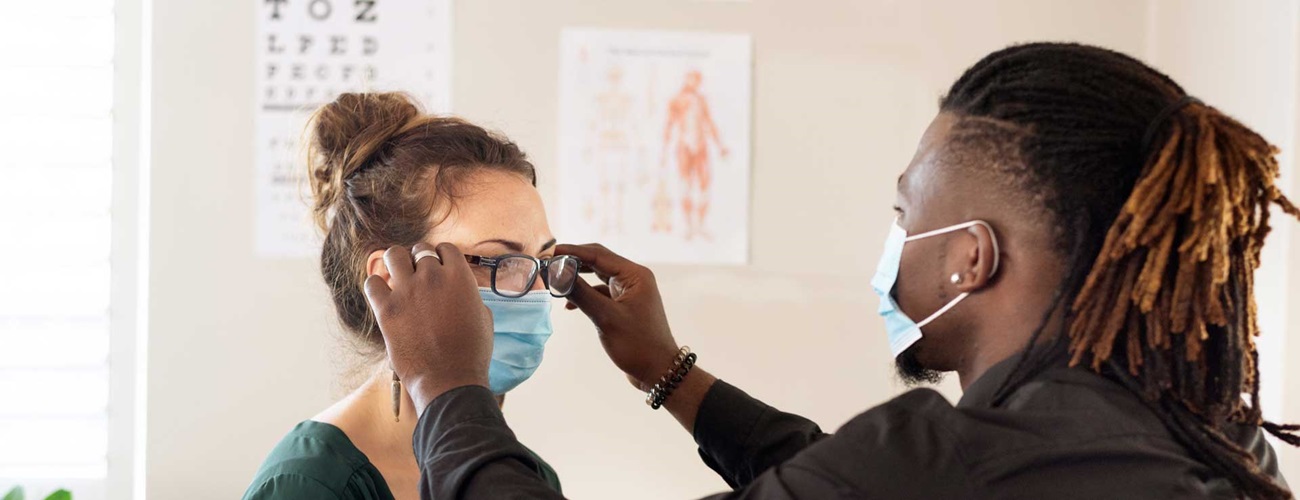
Diagnosis of Myopia
Myopia can be diagnosed during a general eye exam by a:
- Visual acuity test to measure vision at distances
- Refraction test to determine the correct prescription for glasses
- Slit-lamp exam to assess the structures of the eyes
Treatment Options for Myopia
- Eyeglasses
- Contact lenses
- Corneal based corrective laser surgery, such as laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) or photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
- Lens-based surgery using a special intraocular lens implant
- Topical atropine drops to slow the progression of childhood nearsightedness
- Orthokeratology contact lenses, which are worn overnight to temporarily re-shape the curvature of the cornea to see clearly the next day after removal of the lenses
Consult with your eye doctor during routine exams to evaluate your risk for developing myopia and to discuss any next steps.