Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
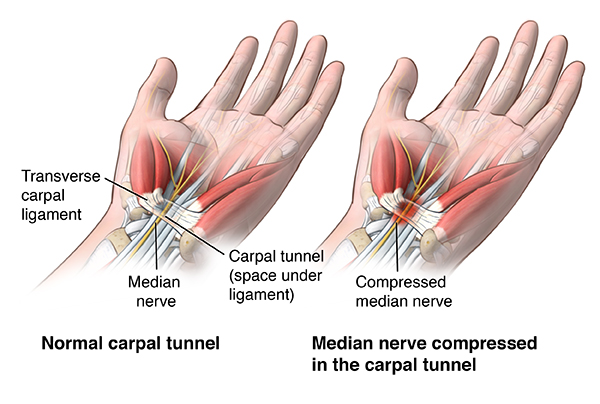
Carpal tunnel syndrome is when the median nerve is compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is an opening in your wrist that is formed by the carpal bones on the bottom of the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament across the top of the wrist. The median nerve provides sensory and motor functions to the thumb and 3 middle fingers. If it gets compressed or irritated, you may have symptoms.
What You Need to Know
- Carpal tunnel release is one of the most common hand conditions requiring surgery.
- Symptoms may include tingling, pain, numbness or weakness in the thumb through ring fingers of the affected hand.
- Women get carpal tunnel syndrome three times more often than men.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a progressive condition that can worsen without proper care.
- Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome often occur during pregnancy and can be alleviated with nonsurgical treatments. Symptoms often improve after delivery, but such patients are at higher risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome later in life.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Causes and Risk Factors
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by an increase in pressure within the carpal tunnel, which leads to compression of the median nerve as it travels across the wrist into the palm through the carpal tunnel.
In most cases, this increase in pressure inside the carpal tunnel is difficult to attribute to one cause. Typically, multiple factors are at play that result in the pressure on the nerve:
- Anatomical changes and differences: The carpal tunnel opening is too narrow
- Some people may have smaller than average carpal tunnel size, which could run in families
- Women, on average, have smaller carpal tunnel size than men and are more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome
- Bones and joints could change shape over time due to diseases such as osteoarthritis or trauma to the wrist
- Swelling and inflammation: When tissues in and around the carpal tunnel swell up, they could press on the median nerve. Swelling and inflammation could result from:
- Frequent, repetitive movements with the hands
- Extending or flexing the wrist for long periods of time
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions that cause inflammation in the joints
- Hormonal or metabolic changes (for example, menopause, pregnancy or thyroid imbalance)
- Other contributing factors:
- Changes in blood sugar levels (may be seen with type 2 diabetes)
- Other conditions or injuries of the wrist (for example, strain, sprain, dislocation or break)
- Obesity
What are the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
These are the most common symptoms:
-
Weakness when gripping objects with one or both hands
-
Pain or numbness in one or both hands
-
"Pins and needles" feeling in the fingers
-
Swollen feeling in the fingers
-
Burning or tingling in the fingers, especially the thumb and the index and middle fingers
-
Pain or numbness that is worse at night, interrupting sleep
The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome may be similar to other medical conditions or problems. Always see your health care provider for a diagnosis.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome | FAQ with Dr. Sophia Strike
(music) >> My name is Sophie Strike and I'm one of the hand and upper extremities surgeon at Johns Hopkins. I see patients with problems of the hand and upper extremity as well as patients who have tumors as I have a specialty in Orthopaedic Oncology.
(music) Carpal tunnel syndrome is actually a compression of one of the large nerves of your arm at the level of the wrist and this can cause numbness, tingling, a burning pain or weakness of your fingers as this nerve controls some of the motion of your hand.
(music) Often, carpal tunnel syndrome can be diagnosed with our clinical examination alone. If the diagnosis is not clear, we may refer patients to have a nerve conduction study as well.
(music) The treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome range from non-invasive treatments such as splinting or hand therapy to work on ergonomics and nerve gliding exercises to injections which may also provide diagnostic information or, for persistent or severe cases, patients may require surgery.
(music) (muffled speaking) For patients who have long-term symptoms, numbness that does not go away or start to have motor weakness in their hand, those are patients that we are more aggressive with pursuing surgery.
(music) Often, the procedure can be done with light sedation and local anesthesia only so patients usually do not require full general anesthesia. After the procedure, they’ll have a soft dressing in place and can go home the same day. Your fingers are free to move and you may have some soreness in your wrist but, generally, patients get back to regular activities after about two to four weeks.
(music) The long-term prognosis for mild cases is usually a near-full recovery within the first six months. Patients who have long-standing or severe symptoms may require a longer period of time and may not get back a hundred percent of their function that they had before. It can recur although we often see this 10, 15 years down the line and that can be treated if it comes up.
(music)
How is carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosed?
Your provider will check your medical history and give you a physical exam. He or she may recommend that you have electrodiagnostic tests on your nerves. These tests are the best way to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome. Electrodiagnostic tests stimulate the muscles and nerves in your hand to see how well they work.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
Your health care provider will figure out the best treatment for you based on:
-
Your age
-
Your overall health and medical history
-
How bad your wrist is right now
-
How well you tolerate specific medications, procedures, or therapies
-
How bad the disease is expected to get
-
Your opinion or preference
Treatment may include:
-
Splinting your hand. This helps keep your wrist from moving. It also eases the compression of the nerves inside the tunnel.
-
Anti-inflammatory medication. These may be oral or injected into the carpal tunnel space. These reduce the swelling.
-
Surgery. This eases compression on the nerves in the carpal tunnel.
-
Worksite changes. Changing position of your computer keyboard or making other ergonomic changes can help ease symptoms.
-
Exercise. Stretching and strengthening exercises can be helpful in people whose symptoms have gotten better. These exercises may be supervised by a physical or occupational therapist.
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome is usually done as an outpatient. Two types of carpal tunnel surgery are done: open surgery and endoscopic surgery. You may have local or general anesthesia, or both, for either surgery.
During open surgery, the surgeon cuts open your wrist. The tissue that is pressing on the nerves is cut. This relieves the pressure on the nerve.
During endoscopic surgery, the surgeon puts a long, thin rod through a tiny cut on the wrist. The rod, or scope, contains a camera and a light. The scope lets the surgeon to see inside your wrist. He or she cuts the tissue using tiny surgical tools.
After the surgery, your hand and wrist are wrapped and put into a splint. This will help to keep you from moving your wrist during your recovery. You will need to wear the splint for a week or two. You will probably have some pain after your surgery. It's usually controlled with pain medication taken by mouth. You may also be told to sleep with your hand elevated to help ease swelling.
Recovery from carpal tunnel surgery is different for each person. If your nerve has been compressed for a long time, recovery may take longer. You will be encouraged to move your fingers and wrist a few days after surgery to help prevent stiffness.
You may need to adjust your work or home activities while you recover. Talk with your health care provider about what you need to change.