Knee Pain and Problems
Knee pain is a common complaint among adults and most often associated with general wear and tear from daily activities like walking, bending, standing and lifting. Athletes who run or play sports that involve jumping or quick pivoting are also more likely to experience knee pain and problems. But whether an individual’s knee pain is caused by aging or injury, it can be a nuisance and even debilitating in some circumstances.
What You Need to Know
- The most common causes of knee pain are related to aging, injury or repeated stress on the knee.
- Common knee problems include sprained or strained ligaments, cartilage tears, tendonitis and arthritis.
- Diagnosing a knee injury or problem includes a medical examination and usually the use of a diagnostic procedure(s) such as an x-ray, MRI, CT scan or arthroscopy.
- Both non-operative and surgical treatment options are available to treat knee pain and problems depending on the type and severity of the condition.
.png?h=198&iar=0&mh=360&mw=520&w=200&hash=3BFCF1966926A5FE6608F088EE7E472C)
Brief anatomy of the knee
The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities, such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities, such as jogging and aerobics.
The knee is formed by the following parts:
-
Tibia. This is the shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg.
-
Femur. This is the thighbone or upper leg bone.
-
Patella. This is the kneecap.
Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
There are 2 groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles (located on the front of the thighs), which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles (located on the back of the thighs), which bend the leg at the knee.
Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. Some ligaments on the knee provide stability and protection of the joints, while other ligaments limit forward and backward movement of the tibia (shin bone).
What are some common knee problems?
Many knee problems are a result of the aging process and continual wear and stress on the knee joint (such as, arthritis). Other knee problems are a result of an injury or a sudden movement that strains the knee. Common knee problems include the following:
-
Sprained or strained knee ligaments and/or muscles. A sprained or strained knee ligament or muscle is usually caused by a blow to the knee or a sudden twist of the knee. Symptoms often include pain, swelling, and difficulty in walking.
-
Torn cartilage. Trauma to the knee can tear the menisci (pads of connective tissue that act as shock absorbers and also enhance stability). Cartilage tears can often occur with sprains. Treatment may involve wearing a brace during an activity to protect the knee from further injury. Surgery may be needed to repair the tear.
-
Tendonitis. Inflammation of the tendons may result from overuse of a tendon during certain activities such as running, jumping, or cycling. Tendonitis of the patellar tendon is called jumper's knee. This often occurs with sports, such as basketball, where the force of hitting the ground after a jump strains the tendon.
-
Arthritis. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis that affects the knee. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative process where the cartilage in the joint gradually wears away. It often affects middle-age and older people. Osteoarthritis may be caused by excess stress on the joint such as repeated injury or being overweight. Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect the knees by causing the joint to become inflamed and by destroying the knee cartilage. Rheumatoid arthritis often affects persons at an earlier age than osteoarthritis.
Seminar Management of Knee Arthritis
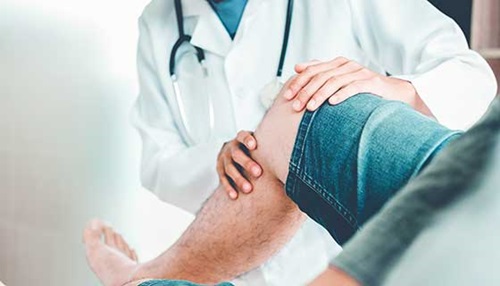
How are knee problems diagnosed?
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, other tests for knee problems may include:
-
X-ray. This test uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This test uses large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body; can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography scan (also called a CT or CAT scan). This test uses X-rays and computer technology to make horizontal, or axial, images (often called slices) of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube (arthroscope), which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen; used to evaluate any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joint; to detect bone diseases and tumors; to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
-
Radionuclide bone scan. A nuclear imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the patient's bloodstream to be detected by a scanner. This test shows blood flow to the bone and cell activity within the bone.
Treatment for knee problems
If initial treatment methods do not provide relief, and X-rays show destruction of the joint, the orthopaedist may recommend total joint replacement for the knee, also referred to as knee replacement.
ACL Tears in Female Athletes: Q&A with a Sports Medicine Expert

Sports injury prevention isn't a one-stop shop, especially for injuries like ACL tears, which are four to eight times more common among women than men. Discover ways for women to help prevent this common injury.