Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic, progressive disease of the bile duct system. The bile duct system carries bile from the liver and gallbladder into the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum.
Symptoms of PSC
Patients with PSC may not have any symptoms. PSC is usually diagnosed in these patients when a routine blood test shows abnormal liver function. Even as the disease progresses, there still may not be any symptoms. When symptoms do develop, it is a result of an obstruction to the bile flow. Symptoms include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes)
- Itching
- Pain in the right upper part of the abdomen
- Fever, chills
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
PSC Diagnosis
A diagnosis of PSC begins with a comprehensive physical exam, during which you describe your symptoms and medical history. Other diagnostic procedures include:
- Laboratory tests
- Liver biopsy
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- Magnetic resonance cholangiography
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests will be ordered to evaluate your liver function. Patients with PSC almost always have abnormal results. Usually a simple blood test can determine if you have abnormally elevated levels of certain serums.
Liver Biopsy
A biopsy offers a definitive diagnosis. Your doctor may perform a biopsy to confirm PSC and stage it (determine the level of severity). During a liver biopsy, tissue is removed from your liver and sent to a pathology lab for analysis.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
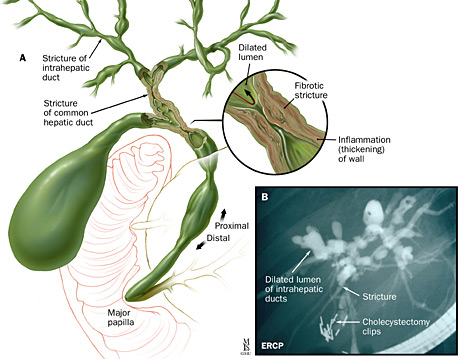
An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an endoscopic technique that allows visualization of the bile and pancreatic ducts. An endoscope is a thin, flexible, lighted tube that is inserted into your mouth to provide access to your upper gastrointestinal system.
During this procedure:
- A special side-viewing endoscope is used to help place the endoscopic tools into the bile and pancreatic ducts.
- A dye is injected into the ducts to highlight any abnormalities.
- An X-ray is taken to see the ducts
ERCP is the preferred method for visualizing the biliary tree (the network of biliary ducts). Your doctor will find many strictures (narrowing) and dilations (opening), which gives the duct its characteristic beaded appearance.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiography
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be useful in detecting blockages. An MRI uses powerful magnetic waves to create a detailed image of the inside of your body. A magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRC) is a specialized MRI used to gather images of the bile ducts.