Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction
Transrectal Ultrasound of the Prostate and Seminal Vesicles

Transrectal ultrasound is performed to visual the prostate, identify a possible ejaculatory duct cyst and evaluate the size of the seminal vesicles. Patients with normal hormones (nl FSH) on laboratory evaluation, normal testes on physical examination, azoospermia (no sperm in the ejaculate) or severe oligozoospermia (extremely low sperm count) are recommended to undergo this testing to rule out ejaculatory duct obstruction.
Needle Aspiration of the Seminal Vesicles
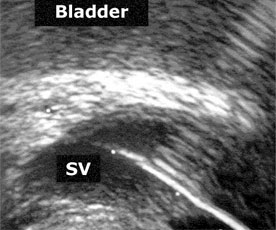
If the seminal vesicles are found to be dilated and/or an ejaculatory duct cyst is visualized, a small needle is placed under ultrasound guidance to aspirate fluid from the seminal vesicles. This fluid is then examined under a microscope for the presence of sperm.
Patients can follow the instructions on prostate biopsy, and should take an antibiotic the day before, the morning of and the day after the procedure to help prevent infection. It is recommended to use a Fleet enema the morning of the procedure to help evacuate stool from the rectum.
It is important that the patient ejaculate within 24 hours before the procedure, preferably the morning of the procedure.
Transurethral Resection of the Ejaculatory Ducts
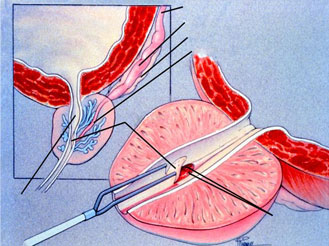
If ejaculatory duct obstruction is identified, it is recommended that patients undergo transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts in the operating room as an elective surgical procedure. This procedure would unroof the ejaculatory duct cyst and open the ejaculatory ducts, allowing for normal flow of ejaculate and improvement of semen parameters. This may assist in couples being able to conceive naturally, without assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF/ICSI.





